- PriceNT
- Our price:NT
- Use bonus pointspt.
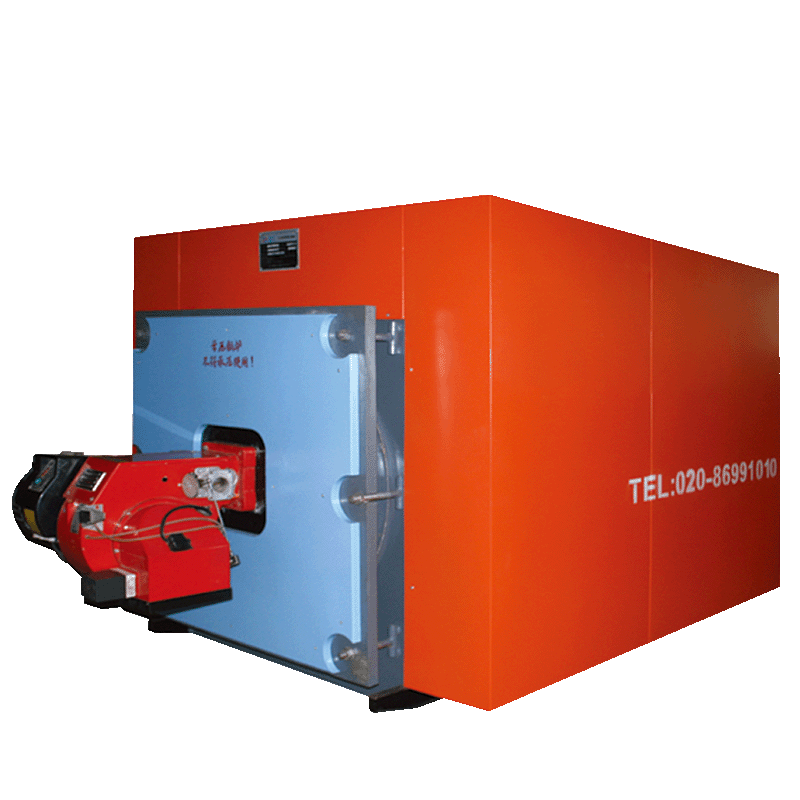
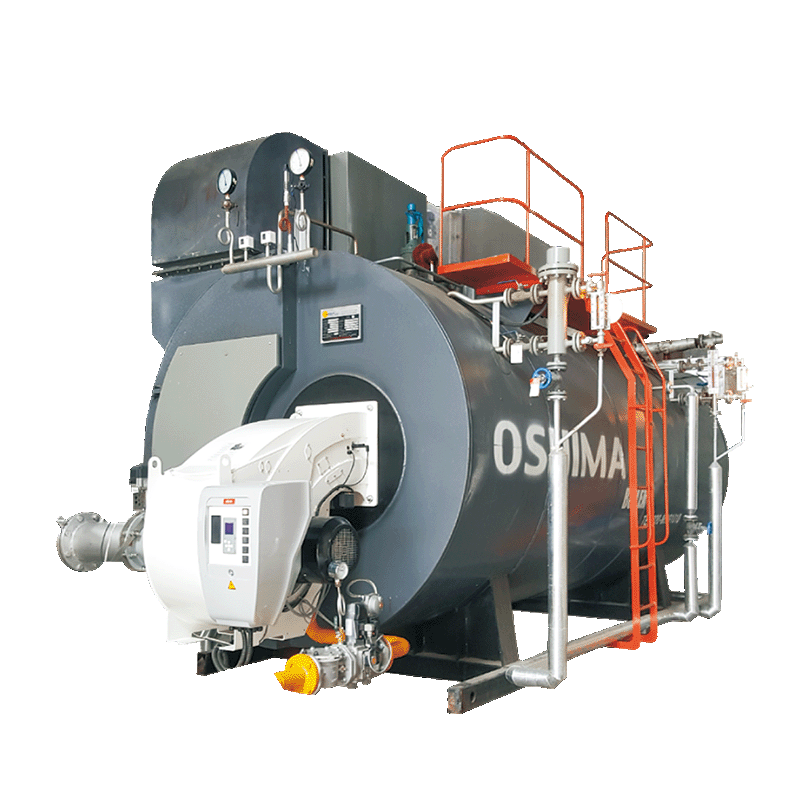
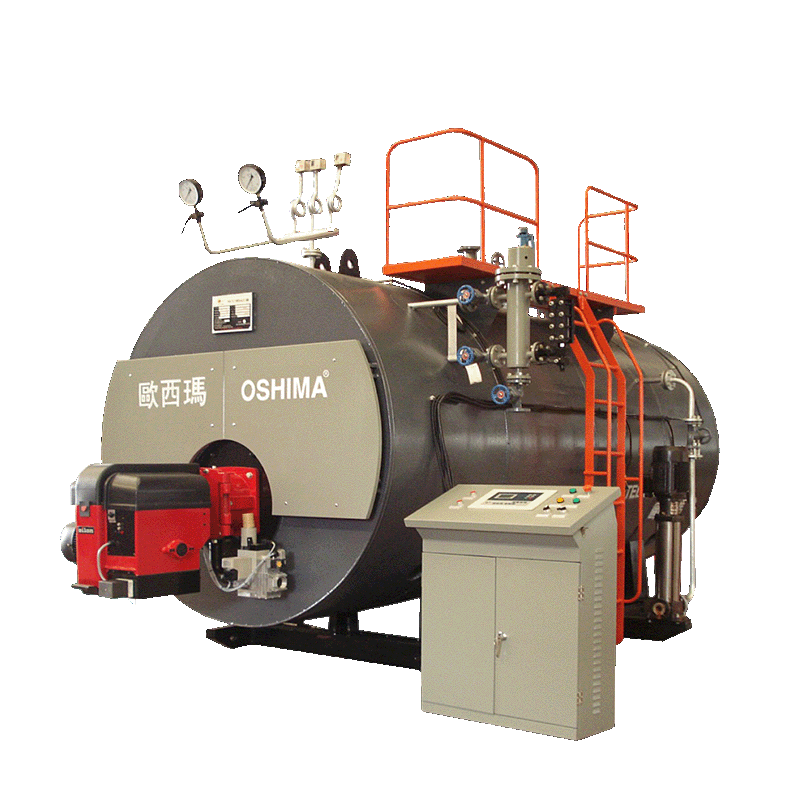
A hot water boiler is a type of heating system that uses hot water as a medium to provide heat to a building or space. It is commonly used for residential and commercial heating purposes. The boiler is designed to heat water and then circulate it through pipes or radiators, delivering the heat to various parts of the building.
Hot water boilers are typically fueled by natural gas, oil, electricity, or propane. The fuel is burned in a combustion chamber, which heats the water in the boiler. The hot water is then circulated through a system of pipes, either through baseboard radiators, radiators, or underfloor heating systems, depending on the specific setup.
The temperature of the hot water is controlled by a thermostat, which triggers the boiler to turn on or off to maintain the desired temperature. Hot water boilers can provide both space heating and domestic hot water for bathing, washing dishes, and other household needs.
Compared to steam boilers, hot water boilers are generally considered more energy-efficient because they don't require the additional energy to convert water into steam. They are also more commonly used in residential applications due to their lower operating pressures and safer operation.
Direct hot water boiler: in a direct hot water boiler, the water used for heating is directly heated within the boiler itself. The boiler contains a heat exchanger that transfers heat from the combustion process to the water. The water is heated and then circulated through the heating system to provide heat.
Direct hot water boilers are generally simpler in design and may be more suitable for certain applications where the demand for hot water is lower or where there are cost considerations.
The choice between direct and indirect hot water boilers depends on factors such as the specific heating requirements, available fuel sources, desired efficiency, and the overall system design.
An atmospheric hot water boiler operates at or near atmospheric pressure, which is the pressure of the surrounding air. These boilers are open to the atmosphere and rely on natural convection to circulate the hot water. Atmospheric boilers are typically used in residential and small commercial applications where the demand for hot water is relatively low. They are relatively simple in design and do not require a pressure vessel.
The main benefit of atmospheric hot water boilers is their inherent safety due to the absence of pressure. The absence of pressure eliminates the risk of explosions or other pressure-related accidents. Additionally, the structure of atmospheric boilers is simpler, which makes installation easier and less complex.
However, atmospheric hot water boilers do have some drawbacks. Since the water inside the boiler is exposed to the atmosphere, it can evaporate over time, resulting in the need for periodic water replenishment. This evaporation can lead to a decrease in water quality. Another challenge is scaling, which occurs on the surface of the water-to-water heat exchanger coil. Scaling limits the efficiency of heat exchange and can shorten the lifespan of the boiler to around 8-10 years.
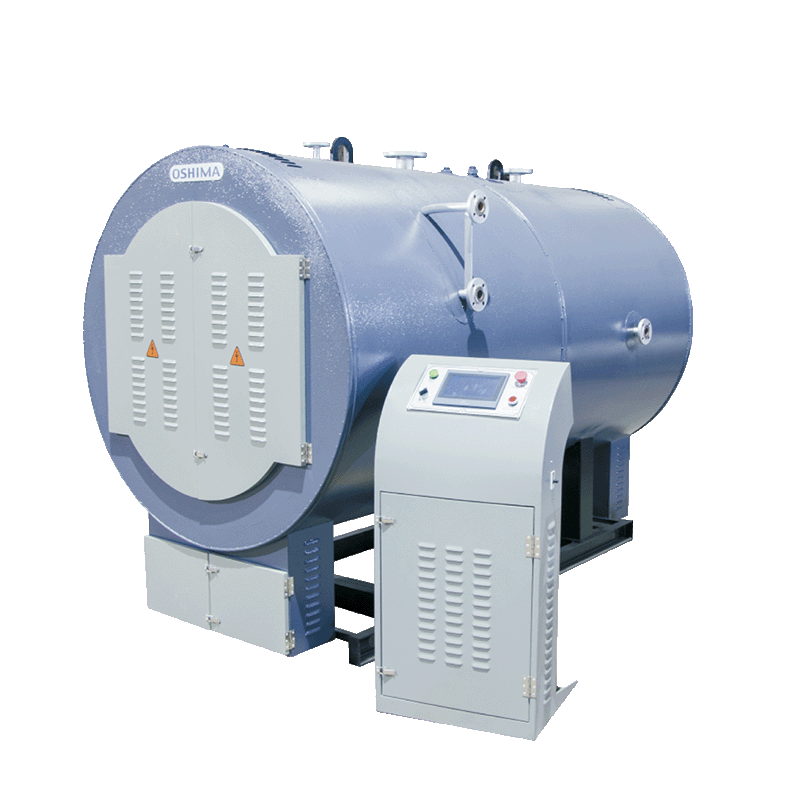
Pressurised systems are usually closed and the water within them is not directly exposed to the atmosphere. These systems can potentially deliver hot water at higher temperatures and are generally more suitable for larger installations or where higher water temperatures are needed.
It's important to consider these factors when choosing a hot water boiler and to conduct regular maintenance, including monitoring water levels and addressing scaling issues, to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Complete combustion system- 100% corrugated furnace with large combustion chamber
Advanced engineering- Thermal efficiency ≥92%
- Automatic control system

Low carbon footprint and eco-friendly- National manufacturing standards-compliant

Investment cost- Auto-feeding system reduces human intervention
 左右滑動看表格
左右滑動看表格| Model | |||||||||||
| CWNS 0.45 | CWNS 0.7 | CWNS 1.05 | CWNS 1.4 | CWNS 1.75 | CWNS 2.1 | CWNS 2.8 | CWNS 4.2 | ||||
| Specification | Heating output | kW | 465 | 698 | 1047 | 1398 | 1745 | 2097 | 2796 | 4194 | |
| *104 Kcal/h | 40 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 240 | 360 | |||
| Rated inward and outward water temperature | ℃ | 95/70 | |||||||||
| Design thermal efficiency | ℃ | <220 | |||||||||
| 25℃ difference hot water output | L/h | 16000 | 24000 | 36000 | 48000 | 60000 | 72000 | 96000 | 144000 | ||
| Design thermal efficiency | % | ≥90 | |||||||||
| Opacity of smoke | Ringelmann chart | <1 (Comply with China national regulations) | |||||||||
| Fuel consumption | Light oil | kg/h | 44 | 66 | 99 | 132 | 165 | 198 | 264 | 396 | |
| Power | Volume | 50HZ.V | 220 | 380 | |||||||
| Burner light oil | kW | 0.74 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 4 | 5.5 | 9.0 | 13.5 | ||
| Overall size | Weight without water | kg | 1220 | 1500 | 2460 | 3242 | 3950 | 4660 | 6543 | 10050 | |
| Weight with water | kg | 1880 | 2430 | 3160 | 4400 | 6150 | 7020 | 10940 | 14000 | ||
- Our price:NT
- PriceNT